자료구조와 함께 배우는 알고리즘 입문을 통해 자료구조 기초를 쌓아보자!
[2장. 기본 자료구조]
1. 배열
- 자료구조 : 데이터 단위와 데이터 자체 사이의 물리적 또는 논리적인 관계
- 데이터 단위는 데이터를 구성하는 한 덩어리. 자료구조는 쉽게 말해 자료를 효율적으로 이용할 수 있도록 컴퓨터에 저장하는 방법.
- 배열 : 같은 자료형의 변수로 이루어진 구성요소가 모인 것
- 배열 본체를 생성하는 본체에 대한 참조를 생성. 본체를 참조하는 배열변수. 인덱스. 배열은 같은 형의 구성요소가 직선 모양으로 속하여 줄지어 있는 단순한 자료구조.
배열의 구성요솟수를 알고 있는 경우 int[] a = new int[5];와 같이 선언한다.
또는 배열의 변수 선언과 본체 생성을 따로 수행하는 것도 가능하다.
//선언하기
int[] a; //a는 자료형이 int형인 배열. 단순한 int형이 아니라 int형인 배열을 명확히 나타내서 더 많이 사용
int a[]; //a는 자료형이 int형인 배열
//참조하기
a = new int[5];//a는 길이가 5인 배열을 참조한다.- new 연산자가 생성하는 것은 배열 본체에 대한 참조
- 구성요소 : 배열 변수 이름[인덱스]
- 구성요솟수 : 배열 변수 이름.length
- 구성요소를 초기화하는 값, 배열을 생성할 때 각 구성요소에 넣어지는 값을 초깃값(default value)라 한다. 배열의 구성요소뿐만 아니라 클래스의 필드(인스턴스 변수와 클래스 변수)도 이 표의 초깃값으로 초기화된다.
-
초기값 : long은 0L, 참조형은 공백참조 또는 null이다. 이 외의 자료형은 아래 표를 참고하자
자료형 초깃값 byte (byte)0 short (short)0 int 0 float 0.0f double 0.0d char '\u0000' boolean false - 값을 대입하지 않은 지역변수 : 메소드 안에서 선언한 지여견수는 초깃값으로 초기화되지 않는다. 자바에서는 초기화나 대입에 의해 값이 넣어져 있지 않은 변수로부터는 값을 꺼낼 수없다. (컴파일 오류 발생)
- 배열의 복제(클론)
- 배열이름.clone()
- 배열을 복제하고 복제한 배열에 대한 참조를 생성.
- 복제한 배열은 원본 배열의 본체가 아니라 그 복제임.
- 배열 요소의 최대값 구하기
- 주사(스캐닝. Scanning) : 배열의 요소를 하나씩 차례로 살펴보는 과정. 주사는 원래 텔레비전 화면이나 사진을 전송할때 화면을 여러개의 점으로 나눠 그점을 전기 신호로 바꾸는 일 또는 이 전기신호에서 점을 조립하여 화면을 재구성 하는 것.
- 메서드의 매개변수로 배열 사용 : 메소드에 매개변수로 전달하는 매개변수는 배열 본체에 대한 참조를 보내는 것.
- 난수를 사용해 배열의 요솟값 설정하기
- 의사난수 : 실제와 비슷한 난수.
- 컴퓨터에서 생성하는 난수는 의사난수. srand 메소드에 전달한 seed값과 컴퓨터 환경이 같다면 결과값이 항상일치하므로 의사난수이다. 이 계산된 결과는 입력값에 의해 결정되므로 seed를 매번 다르게 설정해야한다. 매 순간 바뀌는 현재 시간을 이용하는 것이 일반적이다.
package com.doit.ds.chapter02;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MaxOfArrayRand {
static int maxOf(int[] a) {
int max = a[0];
for(int i=1; i<a.length; i++) {
if(a[i] > max) {
max = a[i];
}
}
return max;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random rd = new Random();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("키의 최대값을 구하기");
//System.out.print("사람 수: ");
//int num = sc.nextInt();
// 연습문제 Q1 : 사람수도 난수로 생성
int num = rd.nextInt(10);
int height[] = new int[num];
for (int i=0; i<num; i++) {
height[i] = 100 + rd.nextInt(90); //난수
System.out.println("height["+i+"]:"+height[i]);
}
System.out.println("최대값:"+maxOf(height));
sc.close();
}
}
- 배열 요소를 역순으로 정렬하기
- 배열의 역순 정렬은 요소교환이 총 n/2회 발생한다.
public class Test {
static final Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
/**
* 연습문제 Q2 배열 요소를 역순으로 정렬하는 과정을 하나하나 나타내는 메소드
*/
static class ReverseAndPrintArray {
//배열 요소 a[idx1]와 a[idx2]의 값을 바꾸기
static void swap(int[] a, int idx1, int idx2 ) {
//출력
for (int i : a) {
System.out.printf("%d ", i);
}
System.out.println();
int temp = a[idx1];
a[idx1] = a[idx2];
a[idx2] = temp;
}
//배열 a의 요소를 역순으로 정렬
static void reverse(int a[]) {
for(int i=0; i < a.length/2; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d와 %d를 교환합니다.\n", a[i],a[a.length-i-1]);
swap(a, i, a.length-i-1);
}
System.out.println("역순 정렬을 마쳤습니다.");
}
}
/**
* 연습문제 Q3
* 배열의 모든 요소의 합계를 반환하는 메소드
*/
static int sumOf(int[] a) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i : a)
sum += i;
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
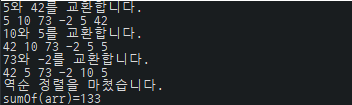
int arr[] = {5, 10, 73, -2, 5, 42};
Test.ReverseAndPrintArray.reverse(arr);
System.out.printf("sumOf(arr)=%d\n",sumOf(arr));
}
}
- 두 배열의 비교
- 두 배열의 모든 요소의 값이 같은지 비교하는 메소드를 구현한 프로그램
public class Test {
/**
* 연습문제 Q4
* 배열a의 모든 요소의 배열b에 복사하는 메소드
*/
static void copy(int a[], int b[]) {
int idx = 0;
for(int i: a) {
b[idx++] = i;
}
}
/**
* 연습문제 Q5
* 배열a의 모든 요소의 배열b에 복사하는 메소드
*/
static void rcopy(int a[], int b[]) {
int idx = a.length-1;
for(int i: a) {
b[idx--] = i;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1, 2, 3};
int[] b = {4, 5, 6};
copy(a, b);
System.out.println("배열 a와 b는 " + (ArrayEqual.equals(a, b) ? "같습니다." : "같지 않습니다."));
rcopy(a, b);
System.out.println("배열 a와 b는 " + (ArrayEqual.equals(a, b) ? "같습니다." : "같지 않습니다."));
}
}

- 기수 변환
- 정수값을 임의의 기수로 변환하는 알고리즘
- 기수 : 수를 나타내는데 기초가 되는 수. 10진법에서는 0~9의 정수
- 서수 : 사물의 순서를 나타내는 수. 첫째, 둘째, 셋째 ...
- 정수 상수의 n진수 표현방법
- 정수 상수는 정수 계열의 값을 나타내는 10진수(Decimal), 8진수(Octal), 16진수(HexaDecimal)를 의미.
- 정수 상수가 0x, 0X로 시작되는 경우 16진수
- 숫자 0으로 시작되는 경우는 8진수
- 두 경우에 모두 해당하지 않으면 10진수로 간주.
public class CardConvRev {
//입력받은 10진수를 2진수 ~ 36진수로 기수 변환하여 나타내기
// 연습문제 Q7 r기수 변환 과정을 자세히 나타내도록 수정
static int cardConvR(int x, int r, char[] d) {
int digits = 0;
String dchar = "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
System.out.printf("%2dㅣ%6d\n", r, x);
do {
System.out.println(" +--------");
d[digits++] = dchar.charAt(x%r); // r로 나눈 나머지를 저장
x /= r; // x=x/r
if (x != 0) {
System.out.printf("%2dㅣ%6d ... %c\n", r, x, d[digits-1]);
} else {
System.out.printf(" %6d ... %c\n", x, d[digits-1]);
}
} while(x != 0);
return digits;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int no; // 변환하는 정수
int cd; // 기수
int dno; // 변환후의 자릿수
int retry; // 재시도
char[] cno = new char[32]; // 변환후 각 자리의 숫자를 넣어두는 문자의 배열
System.out.println("10진수를 기수 변환합니다.");
do {
do {
System.out.print("변환하는 음이 아닌 정수 : ");
no = sc.nextInt();
} while(no < 0);
do {
System.out.print("어떤 진수로 변환할까요?(2~36): ");
cd = sc.nextInt();
} while(cd < 2 || cd > 36);
dno = cardConvR(no, cd, cno);
System.out.print("1. 뒤쪽에서 앞으로 역순으로 스캔 : "+ cd + "진수로는 ");
for(int i= dno-1; i >= 0 ; i--){
System.out.print(cno[i]);
}
System.out.println("입니다.");
// 연습문제 Q6
dno = Test.cardConv(no, cd, cno);
System.out.print("2. 앞에서 순차적으로 스캔 : "+cd + "진수로는 ");
for(int i=0; i<dno; i++) {
System.out.print(cno[i]);
}
System.out.println("입니다.");
System.out.print("한 번 더 할까요? (1.예/2.아니오) : ");
retry = sc.nextInt();
} while(retry == 1);
sc.close();
}
}public class Test{
/**
* 연습문제 Q6
* 배열의 앞쪽에 아랫자리가 아닌 윗자리를 넣어두는 메소드
*/
static int cardConv(int x, int r, char[] d) {
int digits = 0;
String dchar = "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<Character>();
do {
stack.push(dchar.charAt(x%r)); // r로 나눈 나머지를 저장
x /= r; // x=x/r
} while(x != 0);
do {
d[digits++] = stack.pop();
} while(!stack.isEmpty());
return digits;
}
}
- 소수의 나열
- 소수는 2부터 n-1까지의 어떤 정수로도 나누어 떨어지지 않는다.
- 만약 나누어떨어지는 정수가 하나 이상 존재하면 그 수는 합성수.
- 같은 답을 얻는 알고리즘은 하나가 아니다.
- 빠른 알고리즘은 메모리를 많이 요구한다.
- n의 제곱근 이하의 어떤 소수ㄹ도 나누어 떨어지지 않으면 소수.
- 다차원 배열
- 자료형 레벨의 구성요소를 요소(element)라 한다.
- long형을 구성 자료형으로 하는 배열을 구성 자료형으로 하는 배열을 구성자료형으로 하는 배열
long y[][][] = new long[2][3][4];
- 한 해의 경과 일 수를 계산하는 프로그램
- 2차원 배열을 활용해서 어떤 날짜의 그해의 경과일수 구하기
package com.doit.ds.chapter02;
import java.util.Scanner;
//해당년도의 경과 일수를 구함
public class DayOfYear {
static int[][] mdays = {
{31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}, //평년
{31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}, //윤년
};
//서기 year년은 윤년인가 (1:윤년/2:평년)
static int isLeap(int year) {
return (year%4==0 && year%100!=0 || year%400==0) ? 1:0;
}
//서기 y년 m월 d일의 그해 경과 일수를 구함
static int dayOfYear(int y, int m, int d) {
int days = d; //일수
System.out.print(days+"일+ ");
for (int i=1; i<m; i++) {
days += mdays[isLeap(y)][i-1]; //평년이면 0, 윤년이면 1
System.out.printf("%d(idx:%d) " , mdays[isLeap(y)][i-1], (i-1));
}
return days;
}
/**
* 연습문제 Q8
* 변수 i와 days 없이 while문을 사용하여 구현
*/
static int dayOfYearWhile(int y, int m, int d) {
System.out.print(d+"일+ ");
while (--m > 0) {
d += mdays[isLeap(y)][m-1];
System.out.printf("%d(idx:%d) ", mdays[isLeap(y)][m-1], (m-1));
}
return d;
}
/**
* 연습문제 Q9
* 서기 y년 m월 d일의 그해 남은 일수를 구함
*/
static int leftDayOfYear(int y, int m, int d) {
int days = mdays[isLeap(y)][m-1]-d;
for (int i=m; i<12; i++) {
days += mdays[isLeap(y)][i]; //평년이면 0, 윤년이면 1
}
return days;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int retry;
int year, month, day;
System.out.println("특정연도의 경과 일수를 구합니다.");
do {
System.out.print("년:");
year = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("월:");
month = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("일:");
day = sc.nextInt();
System.out.printf("그 해 %d일째입니다.\n", dayOfYear(year, month, day));
System.out.printf("연습문제8: 그 해 %d일째입니다.\n", dayOfYearWhile(year, month, day));
System.out.printf("연습문제9: 그 해 남은 일자는 %d일입니다.\n", leftDayOfYear(year, month, day));
System.out.print("한 번 더 할까요? (1:Y/0:N):");
retry = sc.nextInt();
} while(retry == 1);
sc.close();
}
}
=
- 다차원 배열의 내부
- 행이 다른요소가 연속으로 놓이지 않는다. x[0][3] 다음에 x[1][0]가 저장되는 것이 아니다.
- 빈 배열 : 배열 요솟수가 0.
- 배열요소의 접근 : 만약 0미만 or 배열 요솟수 이상의 인덱스를 사용하면 IndexOutOfBoundException가 발생한다.
2. 클래스
- 클래스란?
- 임의의 데이터형을 자유로이 조합하여 만들 수 있는 자료구조
- 여러형의 요소를 조합하여 만든 자료구조.
- 클래스가 가지는 데이터 요소를 필드.
- 클래스형 변수를 사용하려면 클래스형 변수(실체를 참조하는 변수)를 만들고 실체인 클래스 인스턴스를 생성.
Test a; //Test형의 클래스형 변수 a 선언
a = new Test(); //Test형의 클래스 인스턴스(실체)를 생성
- 클래스에 대한 보충
- 클래스 본체와 멤버
- 클래스 본체에서는 다음과 같은 내용을 선언할 수 있다.
- 맴버(필드, 메서드, 중첩 클래스, 중첩 인터페이스)
- 클래스 초기화. 인스턴스 초기화
- 생성자
- 필드/메서드/생성자를 선언할 때 public/protected/private을 지정할 수 있다.
- 메서드/생성자는 다중으로 정의 가능.(오버로딩)
- final로 선언한 필드는 한 번만 값을 대입할 수있다.
- 생성자는 새로 생성한 인스턴스의 초기화를 위해 사용된다.
- 클래스 본체에서는 다음과 같은 내용을 선언할 수 있다.
- 공개클래스 : public class. 다른 패키지에서 사용할 수 있는 공개 클래스.
- final클래스 : 서브클래스를 가질 수 없다. 새로운 클래스를 상속할 수 없다. 파이널 클래스
- 파생클래스 : 특정 클래스 A를 직접 상위 클래스로 하려면 선언할 때 extends A를 추가해야한다. extends가 없는 클래스의 상위 클래스는 Object클래스가 된다. Object 클래스는 상위 클래스를 가지 않는 유일한 클래스
- 인터페이스 구현 : 인터페이스 X를 구현하려면 선언에 implements X를 추가해야 한다.
- 추상클래스 : 클래스 접근 제한자 abstract를 붙여 클래스를 선언하면 추상 메서들르 가질 수 있는 추상 클래스가 된다. 추상 클래스형은 불완전한 클래스이므로 인스턴스를 만들 수 없다.
- 중첩클래스 : 클래스 또는 인터페이스 안에 선언한 클래스는 중첩 클래스 nested class가 된다.
- 멤버 클래스 : 그 선언이 다른 클래스 또는 인터페이스 선언에 둘러싸인 클래스
- 내부 클래스 : 명시적으로도 암묵적으로도 정적으로 선언되지 않는 중첩 클래스
- 지역 클래스 : 이름이 주어진 중첩 클래스인 내부 클래스. 어떤 클래스의 멤버도 될 수 없다.
- 클래스 본체와 멤버
- 클래스의 배열
package com.doit.ds.chapter02;
//신체검사 데이터용 클래스 배열에서 평균 키와 시력의 분포를 구함
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PhysicalExamination {
static final int VMAX = 21; //시력분포(0.0에서 0.1단위로 21개)
static class PhyscData {
//필드
String name; //이름
int height; //키
double vision; //시력
//생성자
public PhyscData(String name, int height, double vision) {
this.name = name;
this.height = height;
this.vision = vision;
}
//키 평균 구하기
static double avgHeight(PhyscData[] dat) {
double sum = 0;
for (int i=0; i < dat.length; i++)
sum += dat[i].height;
return sum / dat.length;
}
//시력 분포 구하기
static void distVision(PhyscData[] dat, int[] dist) {
int i = 0;
dist[i] = 0;
for (i=0; i<dat.length; i++) {
if(dat[i].vision >= 0.0 && dat[i].vision <= VMAX/10.0)
dist[(int)(dat[i].vision * 10)]++;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
PhyscData[] x = {
new PhyscData("가가가", 162, 0.3),
new PhyscData("나나나", 173, 0.8),
new PhyscData("다다다", 175, 2.0),
new PhyscData("라라라", 171, 1.5),
new PhyscData("마마마", 168, 0.4),
new PhyscData("바바바", 174, 1.2),
new PhyscData("사사사", 169, 0.8),
};
int[] vdist = new int[VMAX]; //시력분포
System.out.println(" 신체검사 리스트 ");
System.out.println("이름 키 시력");
System.out.println("-------------------");
for (int i=0; i <x.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("%-8s%3d%5.1f\n", x[i].name, x[i].height, x[i].vision);
}
System.out.printf("\n평균 키 : %5.1fcm\n", avgHeight(x));
distVision(x, vdist);
System.out.println("\n시력분포");
for (int i=0; i < VMAX; i++) {
System.out.printf("%3.1f ~ :%2d명\t", i/10.0, vdist[i]);
if ((i+1)%5==0) {
System.out.println();
}
}
/**
* 연습문제 Q10
* 시력 분포를 기호문자 *을 이용해 출력되도록 작성
*/
System.out.println("\n\n시력분포(*)");
for (int i=0; i < VMAX; i++) {
System.out.printf("%3.1f ~ : ", i/10.0);
for (int j=0; j<vdist[i]; j++)
System.out.print("*");
if ((i+1)%5==0) {
System.out.println();
} else {
System.out.print("\t");
}
}
sc.close();
}
}
}
package com.doit.ds.chapter02;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 연습문제 Q11
* 서기 년월일을 필드로 갖는 클래스 생성
*/
public class YMD {
int y; //년
int m; //월
int d; //일
static int[][] mdays = {
{31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}, //평년
{31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}, //윤년
};
public YMD(int y, int m, int d) {
this.y = y;
this.m = m;
this.d = d;
}
//서기 year년은 윤년인가 (1:윤년/2:평년)
static int isLeap(int year) {
return (year%4==0 && year%100!=0 || year%400==0) ? 1:0;
}
//n일 뒤의 일자를 반환
public void after(int n) {
//1년 초과 확인
if(n > 365) {
this.y += (n/365);
n %= 365;
}
while(n>0) {
if (n > (mdays[isLeap(this.y)][this.m-1] - this.d)) {
n -= (mdays[isLeap(this.y)][this.m-1] - this.d);
this.m++;
this.d = 0;
} else {
this.d += n;
n = 0;
}
}
print();
}
/* public void after(int n) {
//일자계산
if (n > (mdays[isLeap(this.y)][this.m-1] - this.d)) {
n -= (mdays[isLeap(this.y)][this.m-1] - this.d);
this.m++;
this.d = 0;
} else {
this.d += n;
n = 0;
}
//월 계산
while(n>0) {
if(n > mdays[isLeap(this.y)][this.m]) {
n -= mdays[isLeap(this.y)][this.m++];
} else {
if(this.d+n<mdays[isLeap(this.y)][this.m]) {
this.d += n;
n = 0;
} else {
this.d += n;
n = 0;
}
}
}
}
*/
public void print() {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("일자는 ");
sb.append(this.y).append("년 ")
.append(this.m).append("월 ")
.append(this.d).append("일 입니다.");
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
//n일 앞의 날짜를 반환
public void before(int n) {
//1년 초과 확인
if(n > 365) {
this.y -= (n/365);
n %= 365;
}
while(n>0) {
if (n > this.d) {
n -= this.d;
this.m--;
this.d = mdays[isLeap(this.y)][this.m-1];
} else {
this.d -= n;
n = 0;
}
}
print();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int retry;
int year, month, day;
System.out.println("특정연도의 경과 일수를 구합니다.");
do {
do {
System.out.print("년:");
year = sc.nextInt();
} while (year<0);
do {
System.out.print("월:");
month = sc.nextInt();
} while (month< 0 && month > 12);
do {
System.out.print("일:");
day = sc.nextInt();
} while (day<0 && day>mdays[isLeap(year)][month]);
YMD ymd = new YMD(year, month, day);
System.out.print("현재 일자에서 157일 이후:");
ymd.after(157);
System.out.print("현재 일자에서 430일 이전:");
ymd.before(430);
System.out.print("한 번 더 할까요? (1:Y/0:N):");
retry = sc.nextInt();
} while(retry == 1);
sc.close();
}
}
문제 출처는 Do it! 자료구조와 함께 배우는 알고리즘 입문 자바편 입니다.
연습문제 풀이는 직접 작성하였습니다. 잘못된 부분이 있다면 댓글 부탁드립니다.
'CS > Data Structure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료구조] 스택과 큐 (0) | 2020.02.02 |
|---|---|
| [자료구조] 검색 (0) | 2019.12.05 |
| [자료구조] 알고리즘이란 (0) | 2019.11.09 |
| [자료구조] Heap (0) | 2019.02.12 |
| [자료구조] Map, Set (0) | 2019.02.07 |